An overview of the most frequently used methods of insertion:
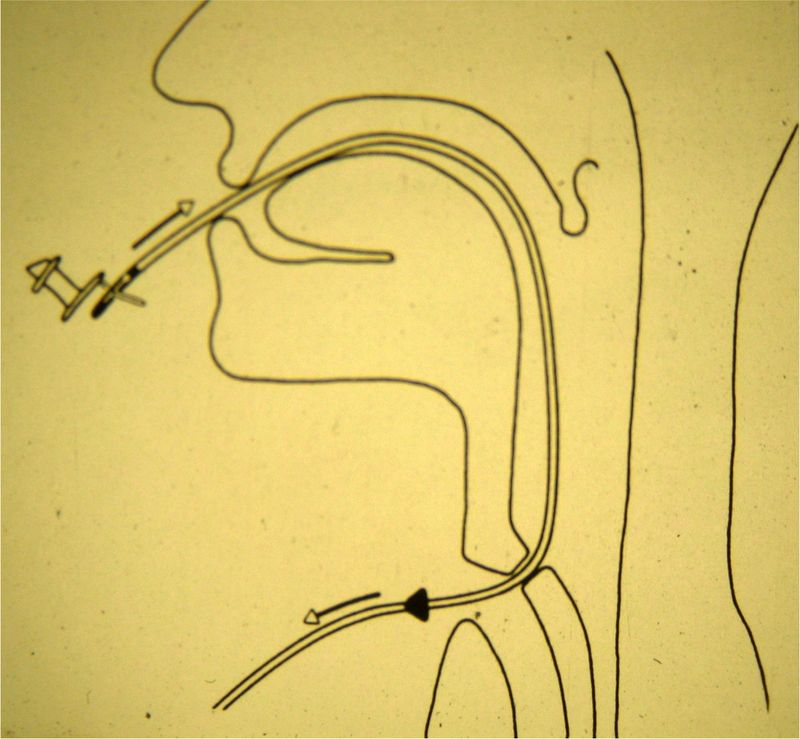
1. Retrograde insertion using a GUIDE WIRE
The guide wire is fed into the esophagotracheal fistula through the tracheostoma and pushed upwards out through the mouth.
The voice prostheses is attached to the tip of the guide wire and pulled into the esophagotracheal fistula. The tracheal flange is unfolded there using surgical clamps.
This procedure is often used for the intraoperative secondary insertion.
It is used with prostheses by various manufacturers.
2. Anterograde insertion using a GEL CAPSULE
Insertion of the voice prosthesis using a gel capsule is an invention by E.D. Blom, and is used with all Blom-Singer® voice prostheses.
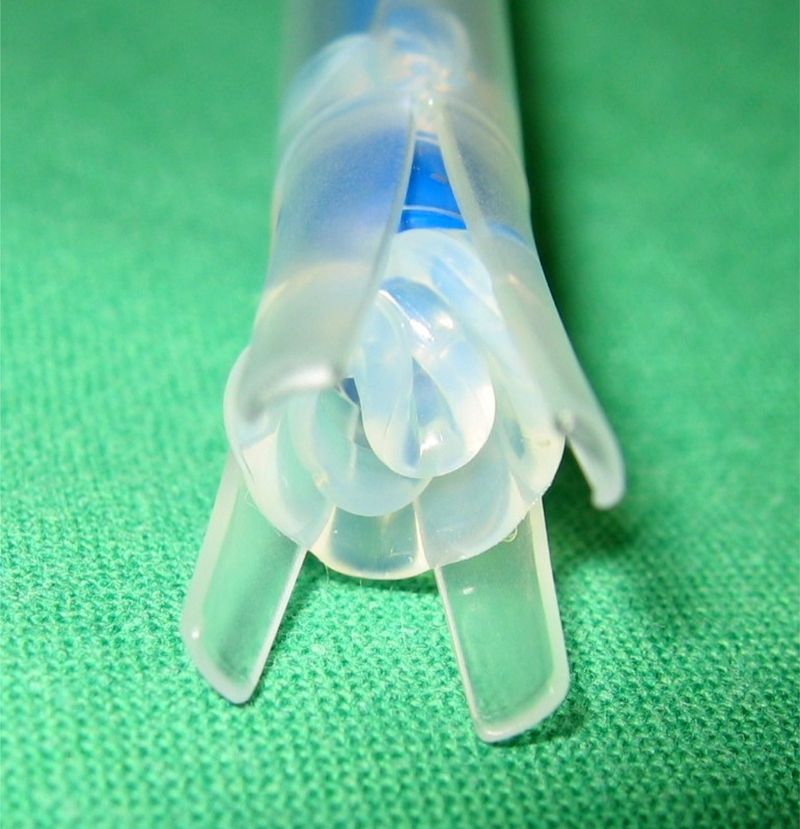
The esophageal flange of the voice prosthesis is folded into a gel capsule. The voice prosthesis is then fed anterograde through the tracheostoma into the esophagotracheal fistula.
Warmth and moisture cause the gel capsule to dissolve and release the esophageal flange. Gel capsules of various sizes are available to suit flanges of various sizes. There is no unfolding of the tracheal flange necessary.
The gel capsule is highly suitable for routine voice prosthesis replacements and the method of choice for changing voice prostheses with small tracheostomas, throat irritations that cause coughing, or shunt problems.
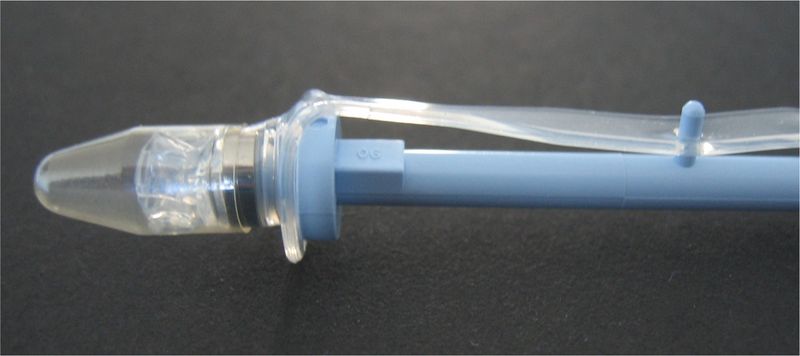
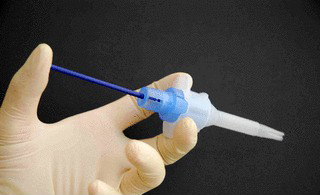
3. Anterograde insertion using an INJECTOR
The esophageal flange of the voice prosthesis is folded into the injector. The injector is then fed anterograde through the tracheostoma into the esophagotracheal fistula, and the voice prosthesis pushed forward. The esophageal flange is released in the esophagus; the injector sleeve is then drawn back and the tracheal flange released.
If the prosthesis is pushed too far into the esophagus (overshooting), the tracheal flange will have to pulled out of the fistula using surgical clamps. The prosthesis can deliberately be pushed too far into the esophagus to achieve a safe positioning of the esophageal flange in the esophagus.
The insertion method using an injector was developed by ATOS MEDICAL®, and is used with the Provox 2 prosthesis and the ActiValve prosthesis. Insertion of a voice prostheses using an injector is highly suitable for routine voice prosthesis replacements.
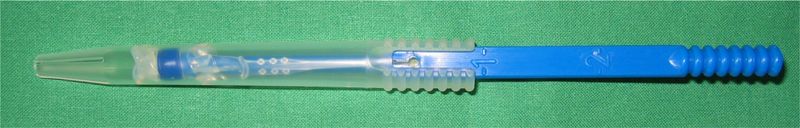
4. Anterograd Insertion with the Provox® SmartInserter™
Der Provox® SmartInserter™ soll den Stimmprotheseneinsatz weiter vereinfachen. Die Stimmprothese ist ab Werk in den Inserter eingelegt und sofort einsatzbereit. Das versehentliche Vorschieben der gesamten Prothese in den Ösophagus wird durch den Inserter verhindert. Die Spitze des Inserters wurde mit atraumatischen "Schwimmhäuten" zwischen den Branchen versehen.
Details zur Funktion des SmartInserter™
Pros and cons of the procedures
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantaged |
|---|---|---|
| Gel capsule | atraumatic quick causes little coughing not so unpleasant | gel remains folding requires practice |
| Injector | quick safe positioning of the esophageal flange | could be traumatic |
| Guide wire | safe positioning of the esophageal flange expulsion via fasa | highly traumatic very unpleasant |
| SmartInserter | safe positioning of the esophageal flange very fast | failures reduced visibility in the stoma |